Intro
JDK8 在并发工具包下增加了LongAdder、DoubleAdder类,提供原子的增减功能。本文主要介绍一下LongAdder,根据Doug Lea的文档描述,该类在高并发的情况下,吞吐量会比AtomicLong高很多,当然会牺牲一定的空间。
AtomicLong
JDK8以前JUC下面的原子类都是通过Unsafe类提供CAS的能力来实现的,而Unsafe类是由C来调用硬件级的原子指令实现的。AtmicLong的部分代码如下:
1 | // setup to use Unsafe.compareAndSwapLong for updates |
Unsafe类部分代码:
1 | public final long getAndAddLong(Object var1, long var2, long var4) { |
getLongVolatile方法是从内存中取到对应的值,然后尝试CAS更新,成功就返回,失败就不断重试直到成功。在高并发的情况下,会造成很大的开销。
LongAdder
先看一下该类的结构;
LongAdder继承自Striped64,其核心功能基本都是Striped64实现的。介绍一下Striped64的主要属性
- 基础值
base - 内部类
Cell1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21@sun.misc.Contended static final class Cell {
volatile long value;
Cell(long x) { value = x; }
final boolean cas(long cmp, long val) {
return UNSAFE.compareAndSwapLong(this, valueOffset, cmp, val);
}
// Unsafe mechanics
private static final sun.misc.Unsafe UNSAFE;
private static final long valueOffset;
static {
try {
UNSAFE = sun.misc.Unsafe.getUnsafe();
Class<?> ak = Cell.class;
valueOffset = UNSAFE.objectFieldOffset
(ak.getDeclaredField("value"));
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new Error(e);
}
}
}
@sun.misc.Contended注解,可以解决伪共享的问题
- 数组
Cells,数组大小为2的N次方,首次初始化为2 NCPU控制数组的最大为cpu的核数
分析
add方法
1 | public void add(long x) { |
longAccumulate方法
先看一下longAccumulate方法大概逻辑;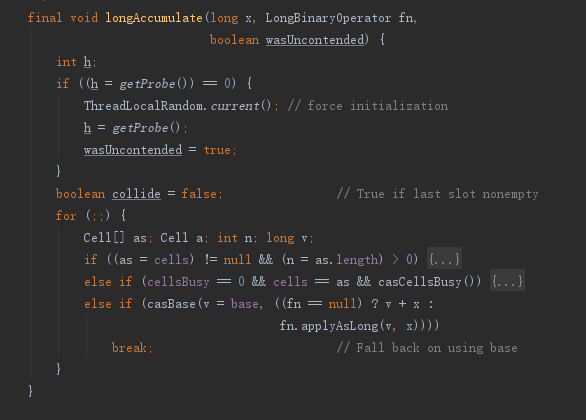
- 首先获取当前线程的
probe如果没有初始化就初始化并设置wasUncontended==true - 循环中的逻辑有三个大分支
- cells数组内有元素
- 尝试扩容
- 尝试用casBase()计算值
1 | int h; |
总结
LongAdder的性能毋容置疑,主要的缺点就是它不能获取自增后的更新值。